The World of Blender - An Overview
Blender is a free and open-source 3D modeling and rendering software that allows users to model, sculpt, texture, rig, animate, and render complex 3D scenes. Its success stems not only from its tremendous feature set, but also from its vibrant community, which is continually adding plugins, lessons, and assets. It began as an in-house app for an animation firm named Neo Geo before being released as its own program. It’s a capable application that has gained popularity in recent years because to its low cost and extensive capabilities for modeling, sculpting, animation, storyboarding, and concept art. Indeed, many people consider it to be on par with professional-level 3D modeling software, which tends to be more expensive.
Because it is open-source, it is an appealing choice because it is regularly updated with official versions and supplemented with independent, community-made plug-ins. Furthermore, Blender provides completely rendered shorts and projects that are free to download so that users can open, analyze, and learn right away.
Despite the foregoing, it is crucial to note that Blender is not a web program; it must be downloaded and installed, and any updates must be obtained and installed from Blender.org. This can also be accomplished via the program’s splash screen by selecting “Blender website” from the links section.
Installation and Configuration
To get started with Blender, get the program from the official website (blender.org) and follow the installation instructions. Blender is available on Windows, macOS, and Linux, ensuring universal accessibility.
The User Interface and Navigation
When you first run Blender, you’ll be met with a visually complex interface. Don’t be daunted! We’ll walk you through the layout, menus, and navigation tools, assisting you in navigating the software.
Exploring 3D Fundamentals
Before diving into complicated animations, it’s critical to first learn the fundamentals of 3D modeling and animation.
Viewport in 3D
Learn how to use the 3D viewport, which is where the magic happens. Learn how to manipulate objects, change views, and use necessary tools to create, alter, and convert 3D scenarios.
Modeling
Learn how to use Blender’s modeling tools to create 3D models. You’ll use techniques like extrusion, subdivision, and sculpting to bring your dreams to life, from simple shapes to sophisticated creations. Blender modeling is the primary way for creating 3D shapes such as people, animals, and objects. This is accomplished by modifying the meshes of predefined shapes, splines, or polygons to create a model, which is done using fundamental shapes such as spheres, cubes, cones, and prisms. There are numerous methods for accomplishing this, such as organic modeling, hard-surface modeling, and low-poly modeling.
Animation Techniques for 2D and 3D Animation Studios US
Blender’s animation skills are central to its appeal, making it a desirable tool for both 2D and 3D animation studios in the United States and elsewhere.
Timeline and keyframes
Set keyframes and manipulate the timeline to learn the principles of animation. This expertise is crucial whether you’re producing a dynamic 2D scene or a complex 3D character animation.
Character Animation and Rigging
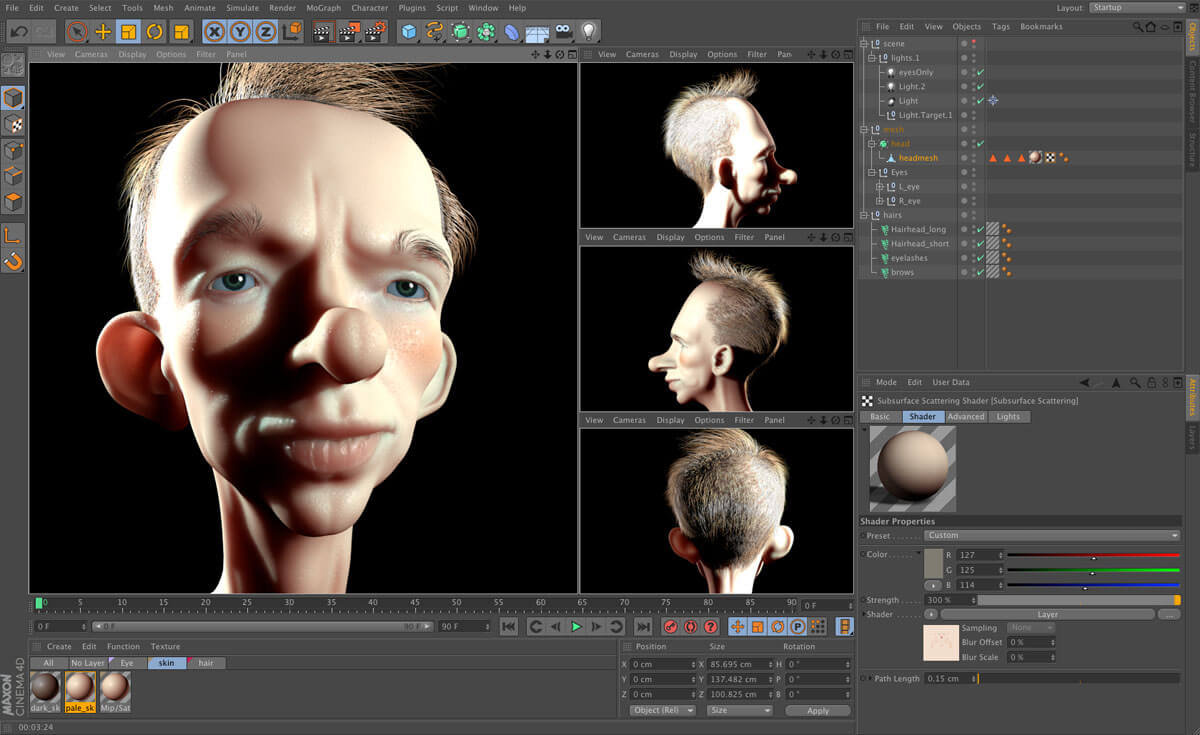
Learn how to rig characters so that they can move and interact realistically. Explore Blender’s sophisticated armature system and character animation techniques to bring your creations to life.
Texturing and Rendering
Texturing and UV Unwrapping
Apply textures to your models to make them more lifelike. Unwrap UVs, paint textures, and create materials to give your sceneries more depth and richness.
Rendering and Output
Explore Blender’s rendering engines to learn how to render your animations and static photos. Choose the best engine for your projects, from EEVEE for real-time rendering to Cycles for photorealism, and export your work in a variety of formats.
Further Exploration and Resources
Advanced Effects and Techniques
Explore advanced techniques such as particle systems, fluid simulations, and dynamic physics to learn more about Blender’s capabilities.
Tutorials and Community
Learn about the growing Blender community, which provides a plethora of lessons, plugins, and assets. There is no shortage of resources to help you on your learning path, from forums to YouTube channels.
Blender is a wonderful 3D software that has transformed the world of animation. Its comprehensive tool set, open-source nature, and active community make it an excellent choice for both new and seasoned artists working in the 2D and 3D animation industries. You’ll be well-equipped to launch on your creative activities and unlock the full potential of Blender if you grasp the essential aspects covered in this guide. So, grab your mouse and keyboard and let your creativity soar in the limitless universe of Blender’s 3D magic.